
Specific Carbon Dioxide Emissions of Various Fuels
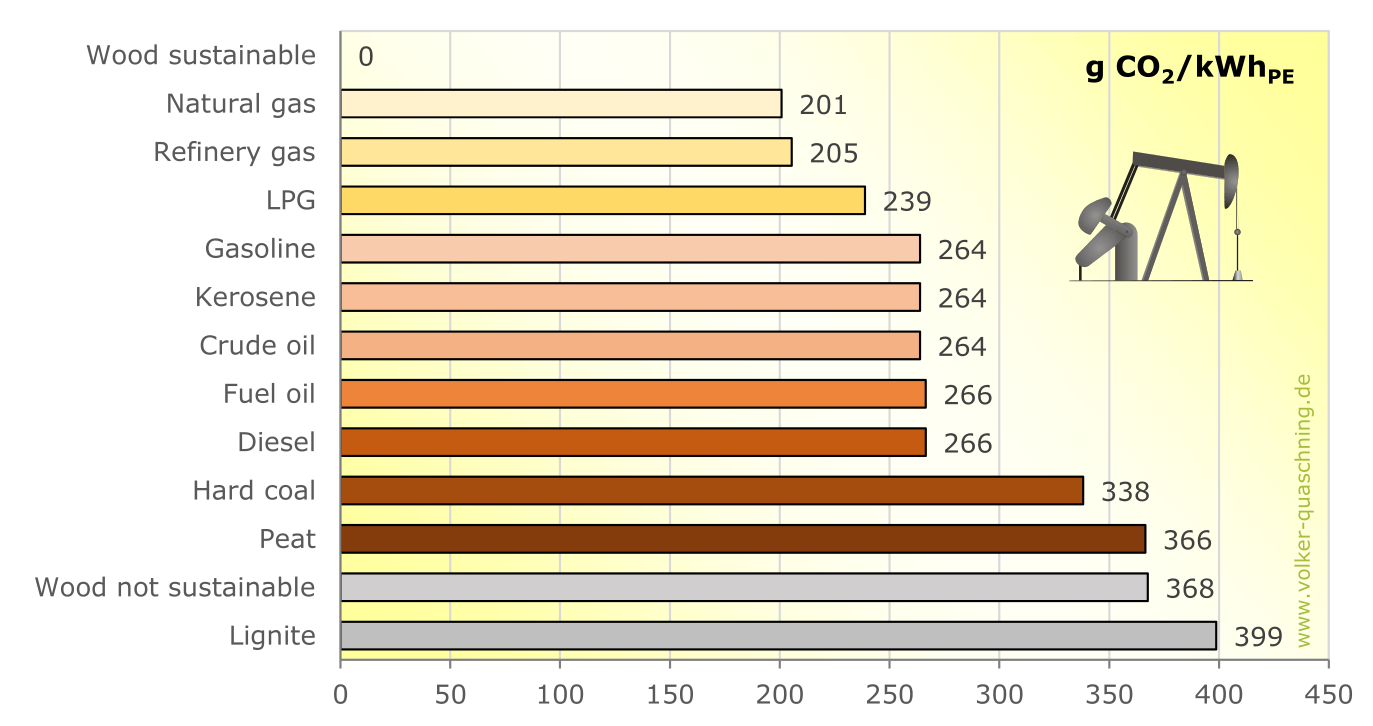
One fuel is not like another - at least when it comes to carbon dioxide emissions. Burning lignite, for example, produces around twice as much carbon dioxide in relation to its energy content as burning natural gas. Natural fuels such as peat and wood also have very high specific emissions if they are not used sustainably. Deforestation therefore has a doubly negative effect on the climate. If the amount of wood burned is limited to the amount that can be regrown, its use is neutral, since wood binds just as much carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as is later released during combustion.
If the fuels are used to generate electricity, carbon dioxide emissions increase opposite proportional with the power plant efficiency. The worse the efficiency of electricity generation, the greater the electricity-specific emissions. For example, if lignite from the german region Lusatia is burned in a power plant with an efficiency of 35 %, 1,14 kg of carbon dioxide is produced per kilowatt hour of electrical energy (kWhel). In a natural gas combined cycle power plant with an efficiency of 60 %, as another example, only 0,33 kg of carbon dioxide is emitted per kWhel.
Replacing lignite-fired electricity with electricity from natural gas can therefore save over 70% of the direct carbon dioxide emissions. In order to properly understand this benefit, the upstream chain emissions and the resulting greenhouse effect must also be taken into account.
Methane, as the main component of natural gas, has a particularly high global warming potential GWP20: Over 20 years of being released to the atmosphere, methane drives global warming by a factor of 84 compared to the same amount of CO2 (IPCC WG1AR5, p.714). Thus, the transport leaks have a high impact on the total GWP of the Natural Gas based power supply and therefore must be considered. Independent surveys of current methane emissions from gas production, transport and use are not yet available for Germany. The following calculation serves as an illustration of the greenhouse effect of natural gas in electricity production, including fugitive methane emissions.
For long-term climate protection, only emission-free energy supply, based on renewable energies and sustainably biomass is an alternative. By getting out of natural gas-fired power generation, it is possible to stop the methane leakage emissions and therefore reduce the global warming potential.
| Fuel | Emissions in g CO2/kWhPE | Emissions in g CO2/MJPE |
| Wood1) | 0 | 0 |
| Wood2),3) | 367.6 | 102.1 |
| Lignite3) | 398.7 | 110.8 |
| ... Lusatia3) | 399.6 | 111.0 |
| ... Central Germany3) | 371.6 | 103.2 |
| ... Rhineland3) | 407.3 | 113.1 |
| Peat3) | 366.5 | 101.8 |
| Hard coal3) | 338.2 | 93.9 |
| Gasoline3) | 263. | 73.3 |
| Fuel oil3) | 266.5 | 74.0 |
| Diesel3) | 266.5 | 74.0 |
| Crude oil3) | 263.9 | 73.3 |
| Kerosene3) | 263.9 | 73.3 |
| Liquid petroleum gas3) | 238.8 | 66.3 |
| Natural Gas3) | 200.8 | 55.8 |
1) in the case of sustainable usage. This includes the compensation of indirect emissions (harvesting, transport, incomplete combustion) and the reduced CO2 storage capacity of the forest. However, in reality, this is only true in exceptional cases.
2) non sustainable usage without reforestation.
3) Source: Umweltbundesamt 2022, Kohlendioxid-Emissionsfaktoren für die deutsche Berichterstattung atmosphärischer Emissionen

"Sustainable Wood" includes the compensation of indirect emissions (harvesting, transport, incomplete combustion) and the reduced CO2 storage capacity of the forest. However, in reality, this is only true in exceptional cases.
Sources: Umweltbundesamt and Fachbuch Regenerative Energiesysteme
| Fuel type | Power Plant Efficiency | direct CO2-emissions1) | Emissions incl. upstream chain2) |
| % | g CO2/kWhel | g CO2‑eq/kWhel | |
| Lignite | |||
| old | 343) | 1173 | 1200 |
| modern | 483) | 831 | 850 |
| mean | 383) | 1049 | 1073 |
| Hard coal | |||
| old | 363) | 939 | 1051 |
| modern | 513) | 663 | 742 |
| mean | 393) | 867 | 970 |
| Natural Gas | |||
| new (turbine) | 39,2 | 512 | 624 |
| new (CCGT) | 59 | 340 | 415 |
| mean | 56,14) | 358 | 436 |
1) Calculated from the primary energy-related CO2 emission factors (excluding upstream chain emissions, excluding other greenhouse gases) divided by power plant efficiency. Source: Umweltbundesamt 2022, Kohlendioxid-Emissionsfaktoren für die deutsche Berichterstattung atmosphärischer Emissionen
2) Calculated from the primary energy-related CO2 emission factors (including upstream chain emissions and other greenhouses gases as CO2 equivalents (CO2‑eq)) divided by power plant efficiency. Source: Umweltbundesamt 2022, Kohlendioxid-Emissionsfaktoren für die deutsche Berichterstattung atmosphärischer Emissionen
3) Mean net electrical efficiency. Source: UBA 2017, Daten und Fakten zu Braun- und Steinkohlen
4) Mean gross electrical efficiency. Source: UBA 2019, Emissionsbilanz erneuerbarer Energieträger 2018
The calculation takes into account direct emissions of CO2 and other greenhouse gases as CO2 equivalents („CO2‑eq“) as well as different leakage losses.
| Leakage losses | Diffuse emissions1) | Diffuse and direct emissions2) |
| g CO2‑eq/kWhel | g CO2‑eq/kWhel | |
| 0% | 0 | 358 |
| 1% | 108 | 466 |
| 2% | 216 | 574 |
| 3% | 324 | 682 |
| 5% | 540 | 898 |
| 10% | 1081 | 1439 |
1) At an efficiency of 56.1 %, about 129 grams of methane are needed to generate one kilowatt-hour of electricity. Each gram of methane has a climate impact (GWP20) of 84 grams of CO2. If only 1 % of the methane escapes additionally, the total emission increases by 0.01∗129∗84=108.4 g CO2‑eq. The upstream emissions have been disregarded here because they already include assumptions about leakage losses. In total, they are reported as 65.8 g CO2‑eq/kWhel.
2) To each of the fugitive emissions are added the 358 grams of CO2 produced by burning 129 grams of methane.
Source: UBA 2022, Emissionsbilanz erneuerbarer Energieträger 2020


 Volker Quaschning und Bernhard Siegel, 11/2022.
Volker Quaschning und Bernhard Siegel, 11/2022.